BIO
135
Identification
Guide to
Cartilage, Bone & Blood Tissues
Return to:
Main Tissues Page ![]() BIO 135 Main Page
BIO 135 Main Page ![]()
|
|
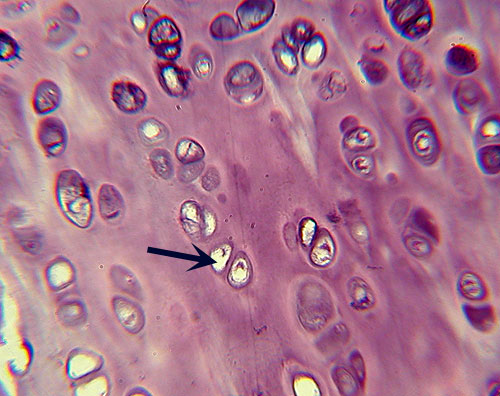
Hyaline Cartilage
Identification: Distinctive lacunae (arrow)
distinguish cartilages from other connective
tissues. Lacunae often are paired. Note lack of fibrous appearance,
instead an overall glassy appearance. Color varies. Features
to Know: chondrocyte in lacuna (arrow). Fibers
Present: collagen fibers (the thin, evenly dispersed fibers do not appear
as fibers, but contribute to an overall glassy appearance). Where
Located: articulating ends of long bones, nose, trachea, ends of ribs.
Functions: structural
support; cushions joints. |
|
|
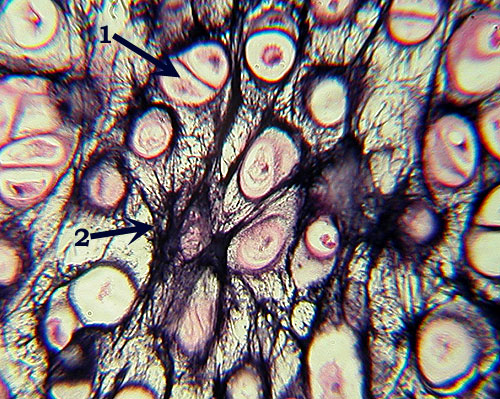
Elastic Cartilage
Identification: Distinctive large, often paired
lacunae (similar to hyaline cartilage), but note extensive dark elastic
fibers (2). Features
to Know: chondrocyte in lacuna (1), elastic fibers
(2). Fibers
Present: elastic fibers (collagen fibers are also present but not
visible). Where
Located: ear lobe, epiglottis (remember those Es!). Function: flexibility,
bendability. |
|
|
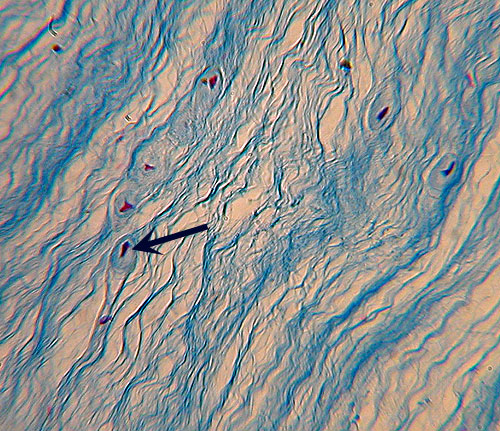
Fibrocartilage
Identification: Distinct, more or less parallel
fibers visible. Distinguished from dense
regular connective tissue by the distinct lacunae (arrow). Features
to Know: chondrocytes in lacunae (arrow). Fibers
Present: collagen. Where
Located: intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee joint. Function: resists
compressive forces. |
|
|
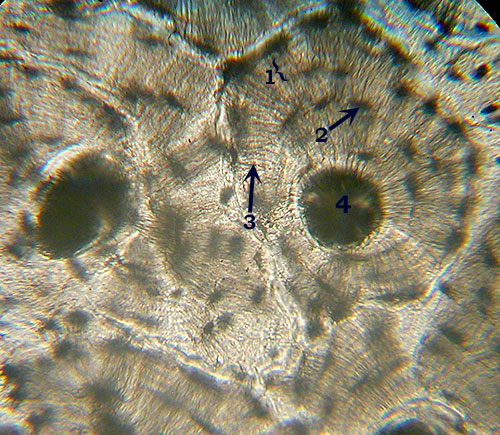
(Compact) Bone
Identification: Concentric rings (like
tree rings) are unmistakable. Features
to Know: lamellae (1), osteocytes in lacunae
(2), canaliculi (3), Haversian
canal (4). An entire set of concentric rings (lamellae) is called a Haversian System. Fibers
Present: collagen fibers present but not visible. Where
Located: bones . Functions: support,
protection, act as levers, mineral storage. |
|
|
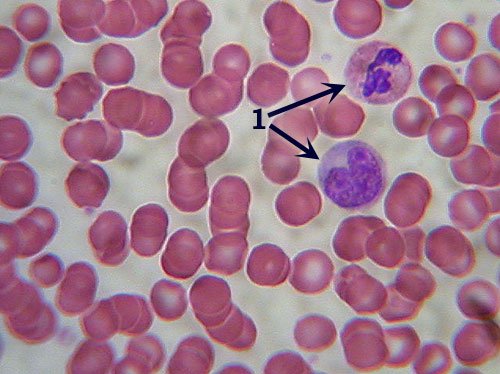
Blood
Identification: The numerous round,
red blood cells in a featureless matrix are unmistakable. Features
to Know: the liquid matrix is called the plasma. The numerous round, red cells are erythrocytes (or red blood cells) that
lack nuclei (the center of the cell is depressed and thus may appear lighter
colored). There are also smaller numbers of larger white cells with large,
multi-lobed nuclei called leucocytes (or white blood cells; 1). Fibers
Present: none visible. Where
Located: within the circulatory system. Functions: transport
of nutrients, gasses, wastes, etc. |
This page created and maintained by Udo M. Savalli. Maintained by Bill D. Snyder. Last updated July 18, 2012