BIO
135 Virtual Labs
Identification
Guide to
Connective Tissue Proper
Return to:
Main Tissues
Page ![]() BIO
135 Main Page
BIO
135 Main Page ![]()
|
|
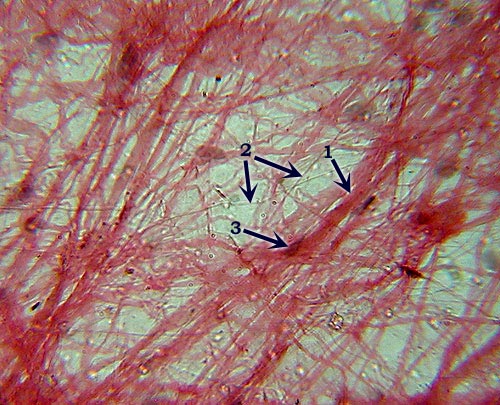
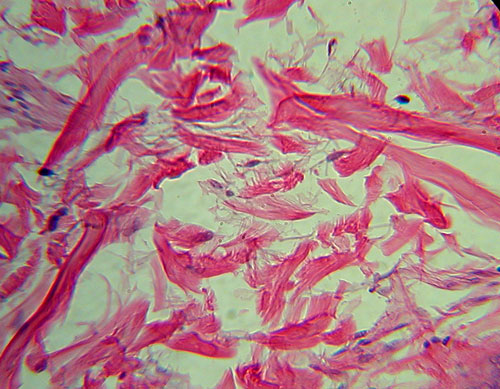
Areolar (or Loose) C.T.
Identification: Loose arrangement of thin (elastic
and reticular) and thick (collagen) fibers that criss-cross haphazardly.
Features
to Know: collagen fibers (1), elastic fibers (2), fibroblasts (3). Fibers
Present: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers. Where
Located: surrounding most organs, underneath epithelia. Functions: wraps, cushions,
holds defensive cells, holds fluids. |
|
|
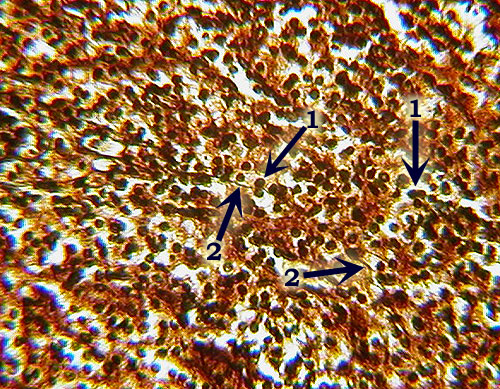
Reticular C.T.
Identification: Dark-staining reticular fibers (2)
present, but may be obscured by the numerous nuclei of lymphoblasts
and other cells (1). Overall brownish color is also distinctive. Features
to Know: lymphoblasts (1). Fibers
Present: reticular fibers (2). Where
Located: spleen (also bone marrow, lymph nodes). Function: forms scaffolding
to support loose cells. |
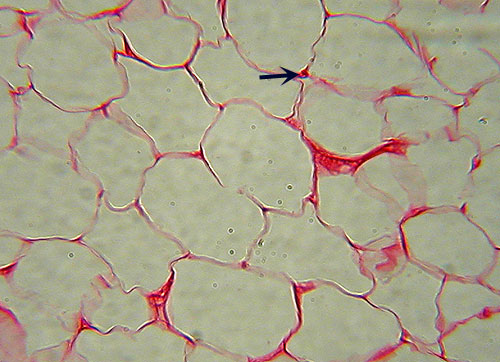
Adipose Tissue
Identification: Virtually no extracellular
matrix visible due to greatly enlarged cells, nearly the entire volume of
which is a fat vacuole (appears empty on slide). Most likely to be
confused with simple squamous epithelium:
note that the "open" areas are surrounded by narrow bands of
cytoplasm, not multiple, nucleated cells. Few nuclei will be visible
(arrow). Features
to Know: adipocyte, nucleus. Fibers
Present: none visible. Where
Located: underneath skin, breasts, surrounding eyes & kidneys. Functions: energy storage,
cushioning, insulation. |
|
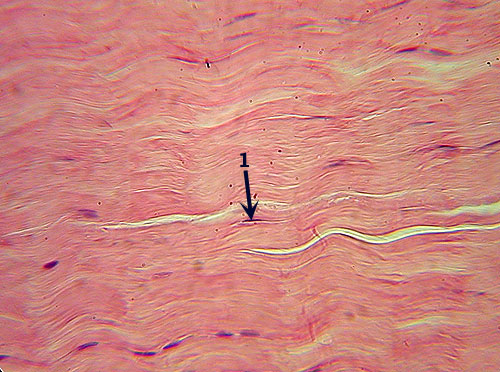
Dense Regular C.T.
Identification: Densely packed parallel fibers.
Note scattered cells (lack of lacunae distinguish this tissue from cartilages;
compare especially to fibrocartilage). Features
to Know: fibroblast (1). Fibers
Present: collagen fibers. Where
Located: ligaments and tendons. Function: attaches
bone to bone or muscle; resists tensile (pulling) forces in single direction.
|
|
|
|
Dense Irregular C.T.
Identification: The collagen fibers are in distinct
bundles, separated by space, giving an overall patchy or blocky appearance
very dissimilar to other tissues. Features
to Know: fibroblasts, if visible. Fibers
Present: collagen fibers. Where
Located: dermis of skin. Functions: provides
strength; can withstand tensile forces in many directions. |
|
|
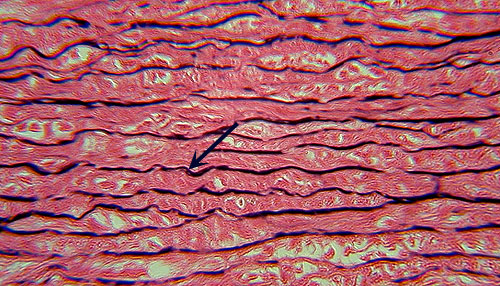
Elastic C.T.
Identification: Similar to dense regular CT (densely
packed collagen fibers), but with distinct dark, usually zigzagging, lines
of elastic fibers (arrow). Although it has a similar name to Elastic
Cartilage, these two tissues are not that similar (note the more parallel
fibers and lack of lacunae here). Features
to Know: fibroblasts. Fibers
Present: collagen fibers, elastic fibers. Where
Located: aorta. Function: elasticity
(can stretch and return to original shape). |
![]()
Continue on to the Cartilage, Bone
& Blood Page
![]()
This page created by Udo M. Savalli.
Maintained by Bill D.
Snyder Last updated September
29, 2009