BIO
135 Tissues Virtual
Identification
Guide to
Muscle and Nervous Tissues
Return to:
Main Tissues Page ![]()
![]() BIO 135 Main Page
BIO 135 Main Page
![]()
|
|
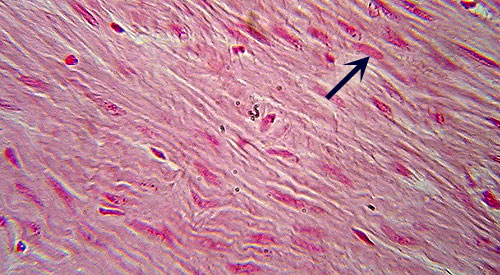
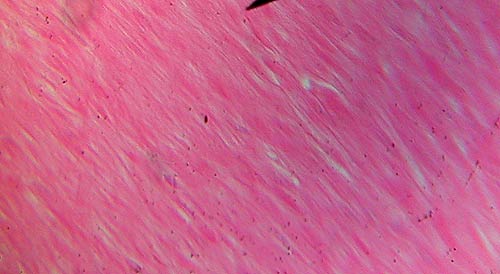
Smooth Muscle
Identification: Muscle cells are packed tightly
together (no gaps between cells) and usually not distinct. Nuclei (arrow) may
or may not be visible. Note lack of striations. Two views are shown. To find
smooth muscle look near the outer portions of the organs on the slides. Features
to Know: nuclei (if visible). Where
Located: under involuntary control; found surrounding most hollow organs.
|
|
|
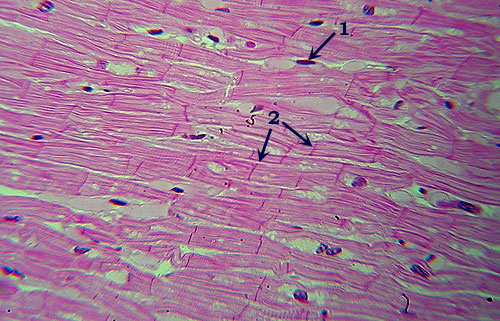
Cardiac Muscle
Identification: Note faint striations across
fibers. Fibers distinct, typically with numerous small gaps between them. Features
to Know: nuclei (1), intercalated disk (2). Where
Located: involuntary muscle of the heart. |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
Identification: Teased or l.s. section shows
distinct, very large, straight fibers (fibers in cardiac muscle are much
smaller & branched). Looks more like hair than any other tissue. Also has
distinct. Features
to Know: striations (1) composed of dark A-bands and light I-bands; nuclei
(2) pushed to edge of fiber; sarcolemna (plasma membrane surrounding fiber). Where
Located: skeletal muscles; under voluntary control. |
|
|
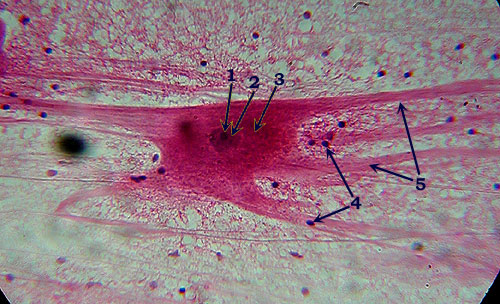
Neuron Smear
Identification: Note distinctive shape of
neuron, with long processes (dendrites and/or axons, 5) extending out from
main cell body. Features
to Know: The large, irregularly shaped cell body (3) contains a darker
nucleus (2), which contains an even darker-staining nucleolus (1). There are also
numerous supporting glial cells, though only their small dark nuclei (4) are
easily seen. |
Continue
on to the Connective Tissue Page
This page created by Udo M.
Savalli. Maintained by Bill Snyder Last updated January 17, 2011.